Morse code is a fascinating method of encoding information using a series of dots and dashes. It is a skill that dates back to the mid-19th century, providing a simple yet effective means of communication. Understanding Morse code can offer various practical applications today, from amateur radio operations to survival situations. This comprehensive guide will explore the translation techniques necessary for mastering Morse code, including basic principles, tools for learning, and advanced strategies for fluency.
Understanding the Basics of Morse Code
The Structure of Morse Code
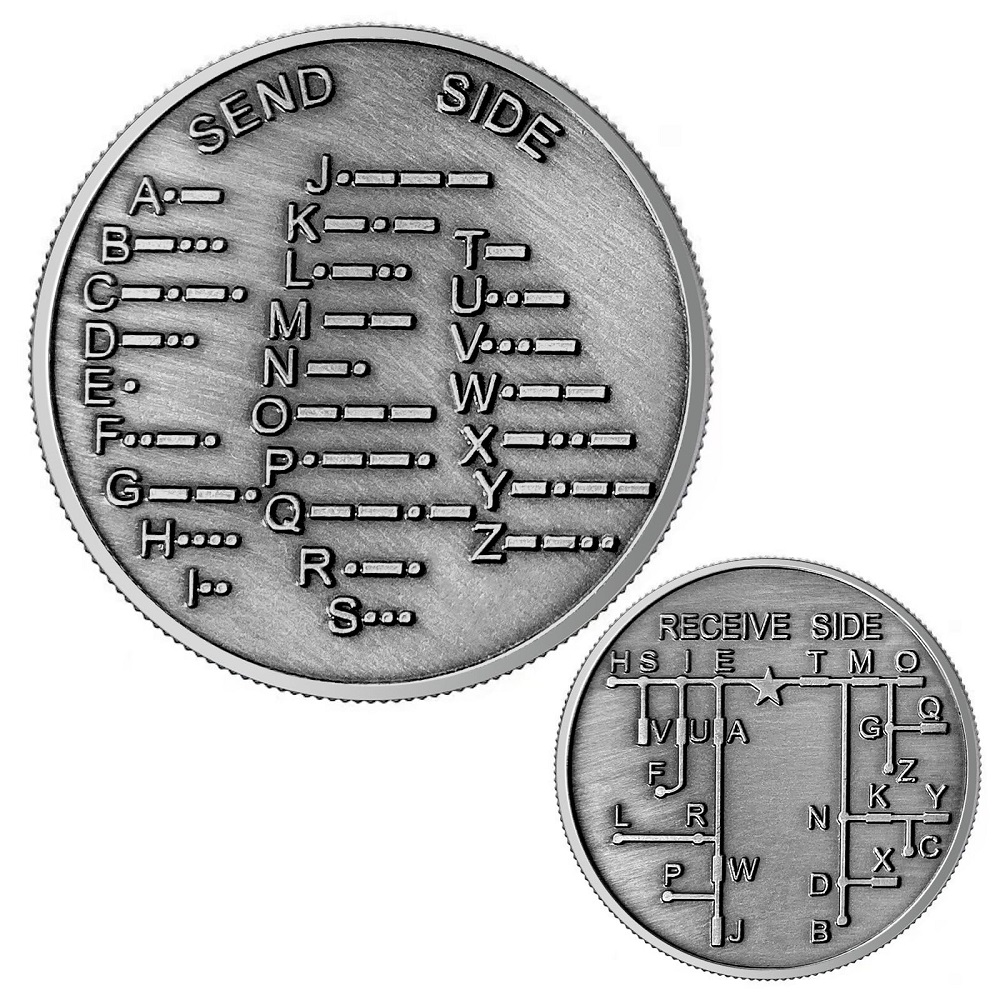
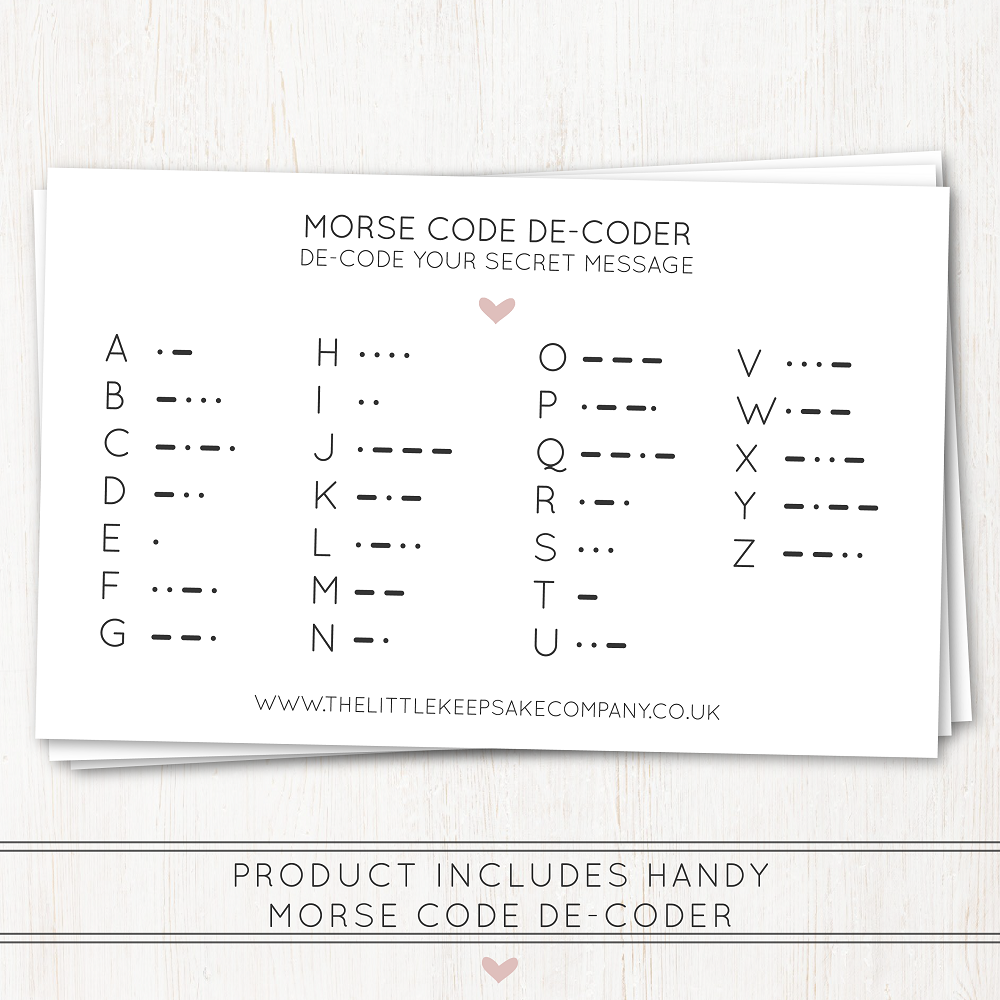
Morse code translates letters, numbers, and punctuation into sequences of short and long signals. These signals are represented as dots (.) for short signals and dashes (-) for long signals. Each letter and number has a unique combination of these signals. For example, the letter “A” is represented as “.-” while “B” is represented as “-…”.
To start learning Morse code, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the Morse code chart. This chart maps each letter of the alphabet and numerical digit to its corresponding Morse code representation. Having a basic understanding of this structure serves as the foundation for further studies and practice.
The History and Relevance of Morse Code
Morse code was developed by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail in the 1830s. It quickly became an essential method of communication, particularly for telegraphy. Though it may seem outdated in today’s digital world, Morse code continues to find relevance in niche applications. For instance, it remains widely used in aviation and amateur radio, where it facilitates reliable communication over long distances.
The historical significance of Morse code enhances its value as a skill. Learners not only gain practical knowledge but also connect with the past. By understanding its origins, one can appreciate the simplicity and effectiveness of Morse code as a communication method.
Techniques for Learning Morse Code
Memorization Strategies
Memorizing Morse code requires dedication and practice. One effective technique is the use of mnemonic devices. Associating Morse code signals with familiar sounds or phrases can aid in recall. For example, the letter “S” (represented by three dots) could be remembered by the phrase “Silly Snakes” to connect the three dots to three “S” sounds.
Flashcards can also be useful tools for memorization. Creating flashcards with the letter on one side and the corresponding Morse code on the other helps reinforce memory. Regular practice with these cards builds familiarity and confidence. Using flashcards during commute times or breaks can further enhance your learning experience.
Regular Practice and Repetition
Repetition is key to mastering Morse code translation(Japanese:モールス信号翻訳). Consistent practice sessions will help solidify your understanding and recognition of Morse code. Try setting aside a few minutes each day to practice. Focus on translating short words or phrases initially, then gradually work your way up to longer sentences.
Learning Morse code does not have to be a solitary journey. Practicing with a partner or joining a Morse code club can enhance the experience. Engaging with others provides opportunities for immediate feedback and the chance to learn from different perspectives. This collaborative approach can accelerate your proficiency and maintain motivation.

Tools and Resources for Learning
Online Resources and Courses
The internet has made it easier than ever to learn Morse code. Numerous websites and online courses offer structured lessons, interactive quizzes, and practice exercises. Websites like Codecademy and YouTube channels dedicated to Morse code provide excellent foundations for beginners.
Mobile applications have also become popular tools for learning Morse code. These apps offer gamified experiences that make practice enjoyable. Many features include flashcards, translation exercises, and audio recognition to aid in learning. With these tools, learners can practice anywhere, and this flexibility encourages consistent engagement.
Books and Reference Materials
In addition to online resources, printed books on Morse code are invaluable. Many books offer detailed explanations of Morse code history, structure, and practical applications. Comprehensive guides often include practice exercises and additional resources for further study.
Keeping a reference chart handy can also be very beneficial. Having a visual representation of Morse code symbols will help you quickly reference and decode messages while you practice. This chart will become a vital tool as you progress in your learning journey.

Mastering the Translation Process
Translating Written Text to Morse Code
When translating written text into Morse code, start with individual letters. Breaking down words into smaller components makes the process more manageable. For example, the word “HELLO” can be divided into its constituent letters: H, E, L, L, O. Each letter can then be translated into its Morse code equivalent: “…. . .-.. .-.. —“.
Practice translating simple words first, gradually working towards more complex sentences. The goal is to develop fluency in both written translation and recognition. With time, you should be able to translate sentences smoothly and quickly without excessive effort.
Receiving and Decoding Morse Code Messages
Understanding how to send Morse code is only one part of the process. Receiving and decoding Morse code messages is equally important. Begin practicing by listening to audio transmissions of Morse code. Focus on recognizing the dots and dashes as they are transmitted.
Using a stopwatch to practice timing is an effective technique for improving your decoding skills. As you listen to Morse code, practice writing down what you hear. Make sure to note the rhythm of the signals, and try to translate them into text afterward. This exercise will help you become more comfortable with the auditory aspect of Morse code.

Advanced Techniques for Proficiency
Timing and Rhythm
Morse code relies heavily on timing and rhythm. Every dot, dash, and space has a specific duration that determines how the signals are interpreted. A dot lasts one unit of time, while a dash lasts three units. The space between letters should last three units, and spaces between words should last seven units. Understanding these timing rules is crucial for effective translation.
To master timing, practicing with a metronome can be beneficial. A metronome helps you develop a consistent rhythm when sending or receiving Morse code. Starting with a slower tempo allows you to focus on accuracy before gradually increasing the speed. Mastery of timing will enhance your overall proficiency.
Engaging with Real-Life Applications
To solidify your skills, try engaging with real-life applications of Morse code. Participate in amateur radio activities or practice with friends who share an interest in Morse code. This engagement encourages consistent usage and provides an opportunity to apply what you’ve learned in meaningful contexts.
Consider exploring how Morse code is utilized in various scenarios. For example, learning how Morse is used in search and rescue operations can reinforce its practical value. Familiarizing yourself with these applications offers insights into the versatility and usefulness of Morse code as a communication tool.
Common Challenges in Learning Morse Code
Overcoming Memory Blocks
Many learners encounter memory blocks when trying to memorize Morse code sequences. If you find yourself struggling to remember certain letters, focus on those specific symbols in your practice sessions. This targeted approach can help reinforce weak areas and improve overall fluency.
Creating stories or images associated with challenging symbols often aids retention. For instance, visualize a character or event that represents the letter “Q” (which is “–.-”). This connection can lead to better memory retention and recall. Experiment with different approaches until you discover what works best for you.
Maintaining Consistency
Another common challenge is maintaining consistency in practice. Life can become busy, leading to interruptions in your study routine. To overcome this, set aside specific times for practice each day or week. Treat these sessions as appointments, ensuring that you prioritize them.
Using reminders and setting goals can help keep you on track. For example, aim to master a number of letters each week. Maintaining a journal to record progress can also provide motivation and help visualize your growth as you move forward in mastering Morse code.
The Value of Mastering Morse Code
In conclusion, mastering Morse code translation techniques can open numerous doors for communication and connection. Understanding its history, structure, and relevance in today’s world enriches your appreciation for this skill. By employing effective learning strategies and utilizing available resources, you can develop proficiency in Morse code.
The journey to learn Morse code is rewarding and helps cultivate patience, persistence, and creativity. Whether you are engaged in amateur radio, enjoy the challenge of decoding messages, or simply wish to connect with history, Morse code offers a unique avenue to explore.
As you develop your skills, you join a community of enthusiasts dedicated to preserving and using this form of communication. In today’s fast-paced digital world, mastering Morse code serves as a reminder of the roots of communication and the art of connection through simpler means. Embrace the practice, enjoy the journey, and let the dots and dashes become a vital part of your communication toolkit.
